SQ LP owerhouse: The Ultimate Guide to Excelling in SQ LS cript!
SQL The management of data in relational databases is facilitated by Structured Query Language. Whether you’re dealing with business data, creating dashboards, or performing complex queries, SQL has your back!
📋 Categories of SQ LC ommands
SQL commands are categorized into categories Five major categories :
Data Manipulation Language (DML) ✍️
DML commands help you Manipulate data Stored in database tables. Conceive DML as the “action” directives
1. SELECT Retrieves information from tables
SELECT e. Name, d. The department name can be obtained by employees who are enrolled in multiple departments before becoming part of the ON team. Department_id = d. Id;
2. INSERT ➕ – Adds new records
Employers (title, job title) VALUES (Jane Doe, Analyst, Developer)
3. UPDATE 🔄 – Modifies existing data
UPDATE employees eGet involved with organizations from ON and beyond. Department_id = d. IdSET e. Salary = e. Salary * 1.05WHERE d. Department_name =' IT ';
4. DELETE Is used to extract data from tables
Eliminate employees FROM departments that are classified as sales
Data Definition Language (DDL) 🏗️
DDL commands are utilized to perform specific actions Elucidate, adjust, or omit database structures Including tables, indexes, and schemas
1. CREATE Creates new tables, views, and indexes
Employees in the CREAT ET ABLE must have a DAT ED EFAULT, CURRENT_DATE, and DATE of hire);
View active_employees A SS EE NE mployees with' active 'status can be selected by selecting *
2. ALTER Adjusts the layout of a table that already exists
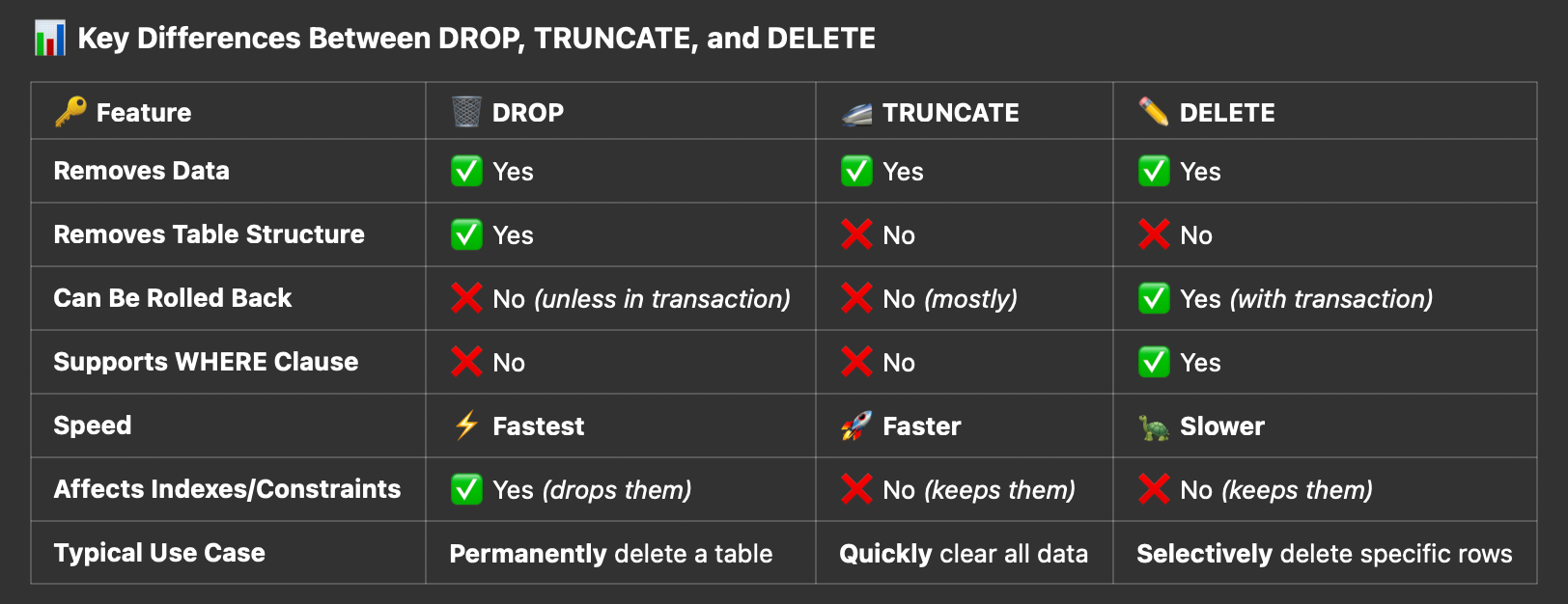
3. DROP Ends tables, views or databases permanently
DRO PT ABLE employees CASCADE;
4. TRUNCATE Removes all data from a table while maintaining its structure
Data Control Language (DCL) 🔐
DCL commands manage Access control and permissions In the database
1. GRANT Provides users with access to information
' user123 'can be accessed through the GRAN TO PTION by selecting employees
2. REVOKE Removes previous authorizations that were granted
Transaction Control Language (TCL) 🔄
TCL commands help manage Database transactions To ensure data integrity
1. COMMIT Restores any modifications made during a transaction
2. ROLLBACK Reverses the effects of changes made during a transaction
SAVEPOINT sp1; For those who are on a salary of 50000, the ID number for UPDATE employees is 1ROLLBAC KT O sp1;
3. SAVEPOINT By using, one can roll back the transaction by inserting a point
4. SE TT RANSACTION ⚙️ – Configures transaction settings
Data Query Language (DQL) 🔍
While SELECT Despite being part of DML, it is frequently classified as an independent module because of its significant significance Querying data
Select the name FROM the employees and type the department's id, which is equivalent to "IT" for departments
🚀 Wrapping Up
Data is managed using SQL commands. Learning DML, DDL, DCL, TCL, and DQL will enable you to become a proficient coder SQL wizard Capable of managing any data problem with ease
