Quick Links
-
Close the Program that You used to access the File
-
Use the Task Manager to close the Application
-
Modify the File Explorer Process Settings
-
Turn off the File Explorer Preview Pane
-
The File in Use is deleted by using the Command Prompt Command
-
Use a Tool to unlock the File in Use
-
Boot Into Safe Mode
If you are unable to view, edit, or delete files in Windows File Explorer, it means that the program is still open in the background or that something did not close correctly. Fortunately, there are some basic techniques that can be used to delete, close, or edit a file
1. Close the Program that You used to access the File
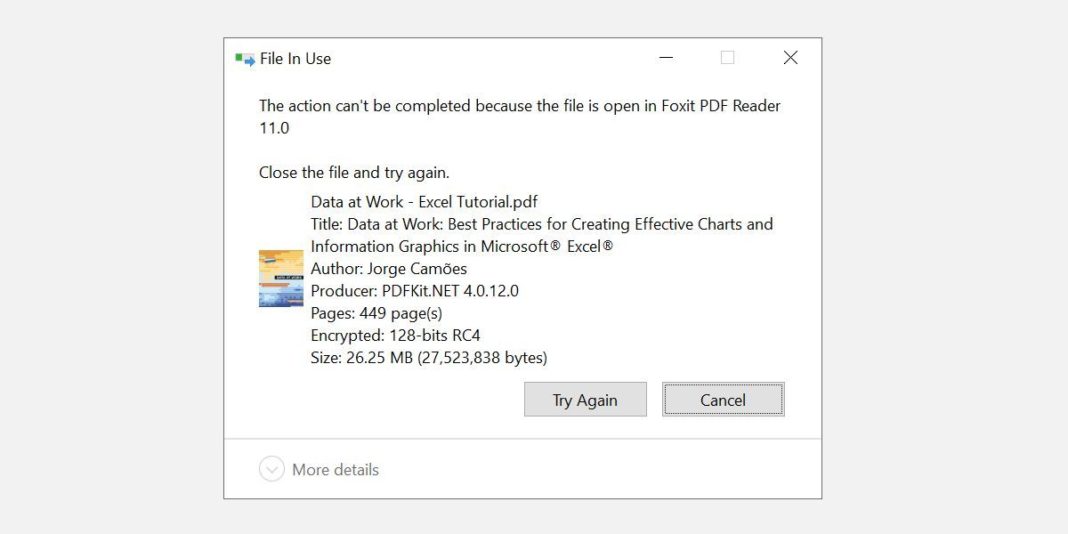
The obvious is the first thing that needs to be addressed. Have you opened a file and not closed it? If the file is closed but the program still runs, then close the application and try again
Examine the system tray to confirm that it was not just minimized
2. Use the Task Manager to close the Application
Task Manager can help Terminate the process or application by hand Your file is being held captive by that. This is one of the most successful methods to fix the “file is open in another program” error, as you may not always be aware that the file did not close properly
Press Ctrl + Shift + ESC Open the Task Manager using your keyboard. Alternatively, you can press Ctrl + Alt + Del Select the menu or right-click the Taskbar and select “Open Task Bar” Task Manager If you’re running Windows 11, the Taskbar won’t open if you right-click it
The compact Task Manager version can be accessed by clicking on it More details Make sure you’re in the bottom left section Processes Tab
Find the application that you employed to open the “file in use” file. If you were viewing a document, search for Microsoft Word

Select the process you want to use and click on it End task In the bottom right. The program will be terminated after this
3. Modify the File Explorer Process Settings
The default setting is for File Explorer to open all its windows in a single operation. Exe). It’s possible that your File Explorer is compelled by default to start multiple processes, potentially resulting in a conflict between processes
Press the Windows key + E To open File Explorer. In Windows 10, go to View> Options> Rename search and folder
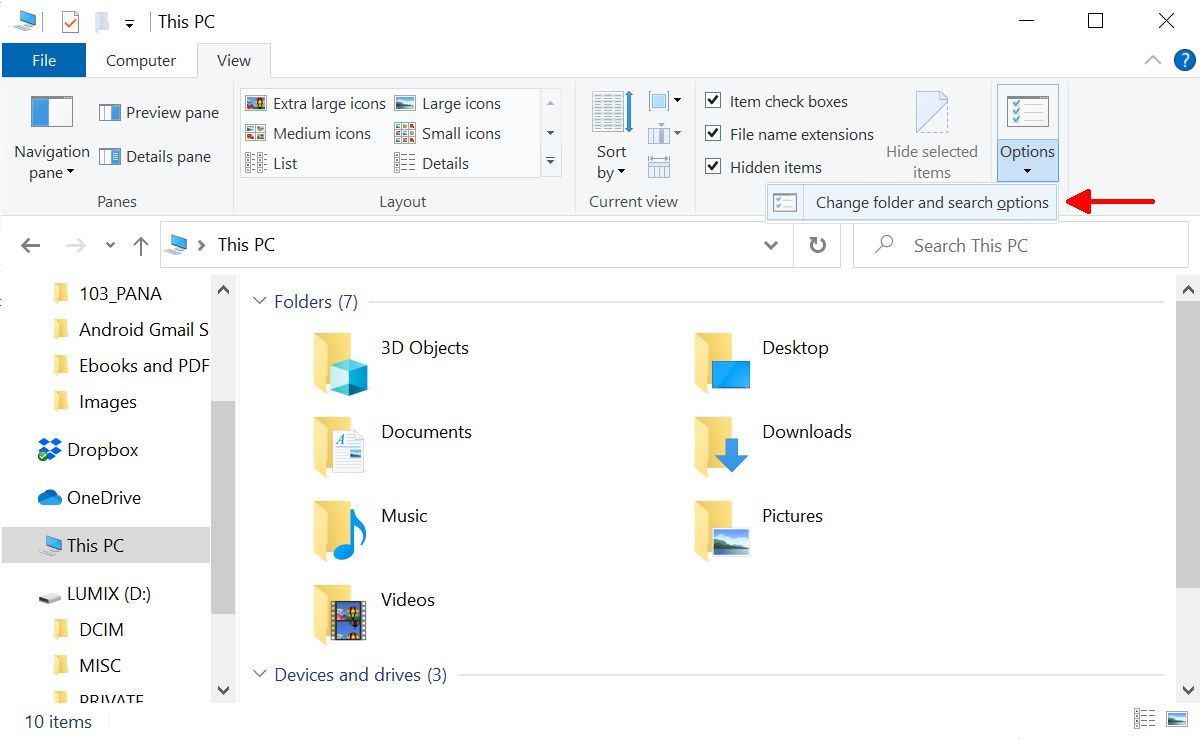
In Windows 11, click the Three-dot “See more” icon Select View below Options
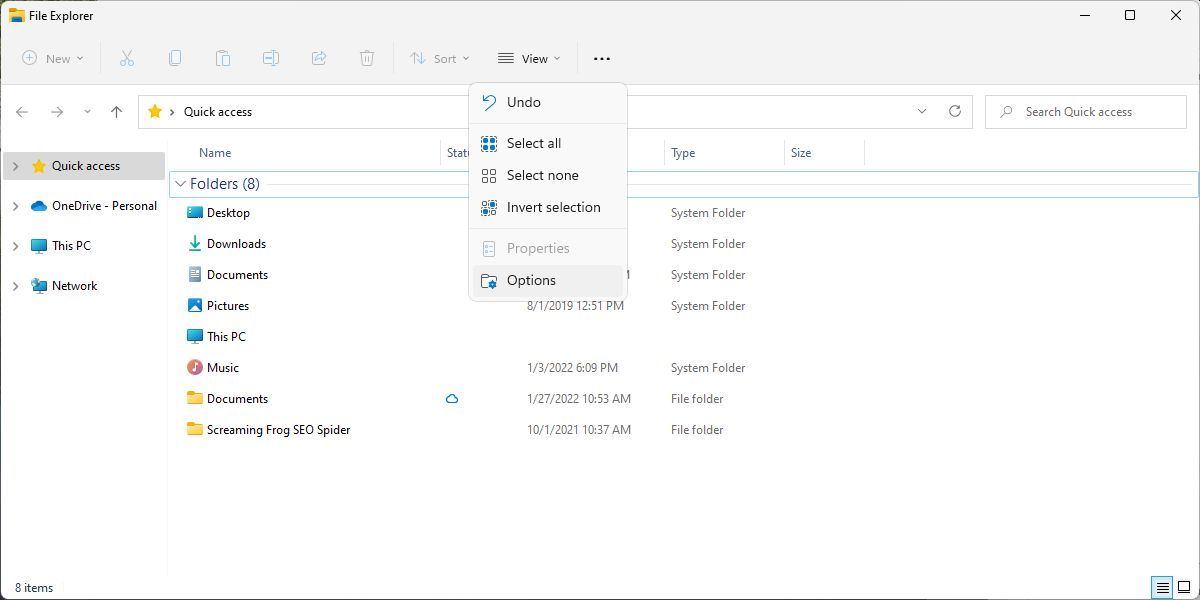
The Folder Options window takes you to the next page View Tab and find the Activate folder windows in a distinct manner Option. Make sure it’s Not checked Click Apply To save any changes

In case the check was not present initially, you should investigate to see if this resolves your problem
4. Turn off the File Explorer Preview Pane
The use of Previews in File Explorer can lead to conflicts, such as the error message “file is open in another program.”
In Windows 10, press the Windows key + E , switch to the View Tab, and press Alt + P To exit the preview pane
Open the File Explorer on Windows 11. Windows key + E ), then go to View> Show , and, if you see a checkmark next to Preview pane , click it to close the preview
The screenshot below displays an open preview pane on the right side of the screen
The “file in use” error is visible only when the operation is restarted after closing the preview pane
5. The File in Use is deleted by using the Command Prompt Command
By using Command Prompt, you can delete the File without access to File Explorer
The first step is to locate the File path directory in File Explorer. Press the Windows key + E To access File Explorer, locate the affected File and copy the File path from the address bar at the top of the window
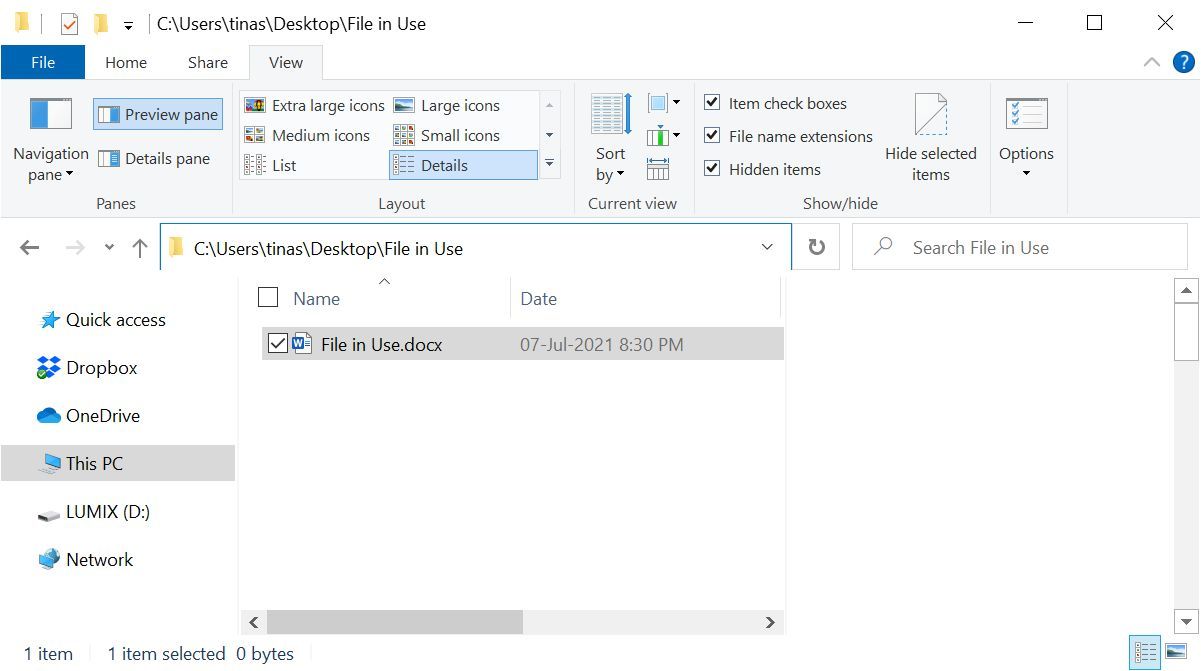
Now right-click the Windows Start button And select Command Prompt (Admin) Or Windows Terminal (admin) To find the file directory of your currently active file, simply enter it Copy the directory path to: Cd And hit Enter
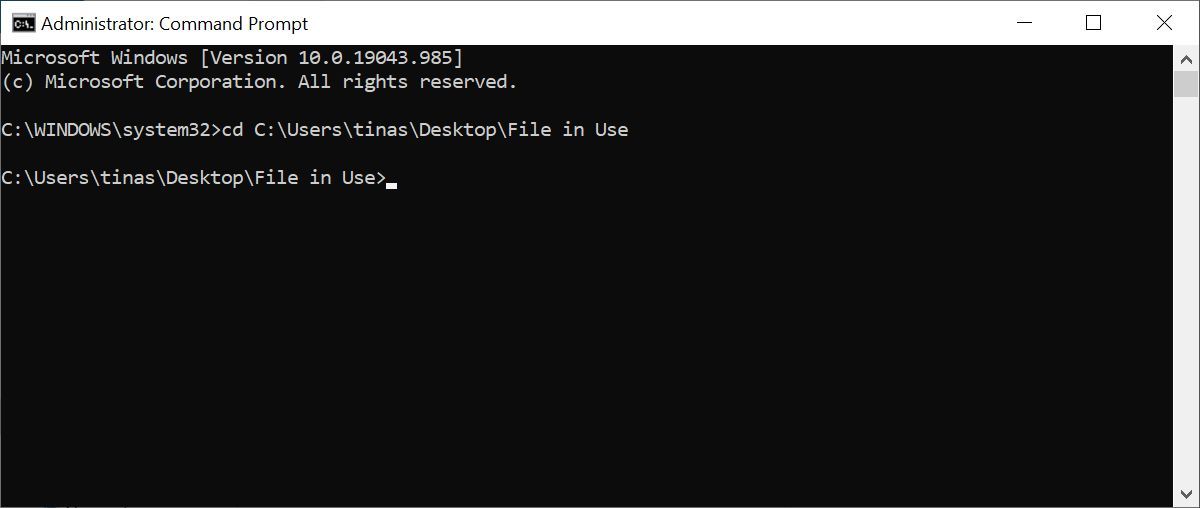
The File Explorer process must be terminated for a temporary period before we can forcefully delete the File that is being used. Your Taskbar, wallpaper, and open folders will be eliminated. Once you’ve restarted File Explorer, all information can be recovered without any difficulty
- Close File Explorer by right-clicking and then selecting OK Ctrl + Shift + ESC To open Task Manager
- Find Windows Explorer The process is located in the list and can be accessed by right-clicking. Select End task
- Return to the Command Prompt window where you initially entered the Command
- Use the following command to delete the file and replace the entire name with the actual file:
Del "file name"
The Task Manager can be used to restart the File Manager Ctrl + Shift + ESC ). Then click File> Run new task , enter Explorer. Exe , and click OK This action will restore your desktop’s normal appearance
6. Use a Tool to unlock the File in Use
If you were unable to manually delete the file or use Command Prompt, you can always use an alternative method Microsoft’s Process Explorer
A more robust version of Task Manager is available that can indicate which process took hold of your file
Click on Process Explorer to open the Search window Find> Find Handle or DLL (or press Ctrl + Shift + F Enter the file name and wait for the list of processes that are currently accessing your file
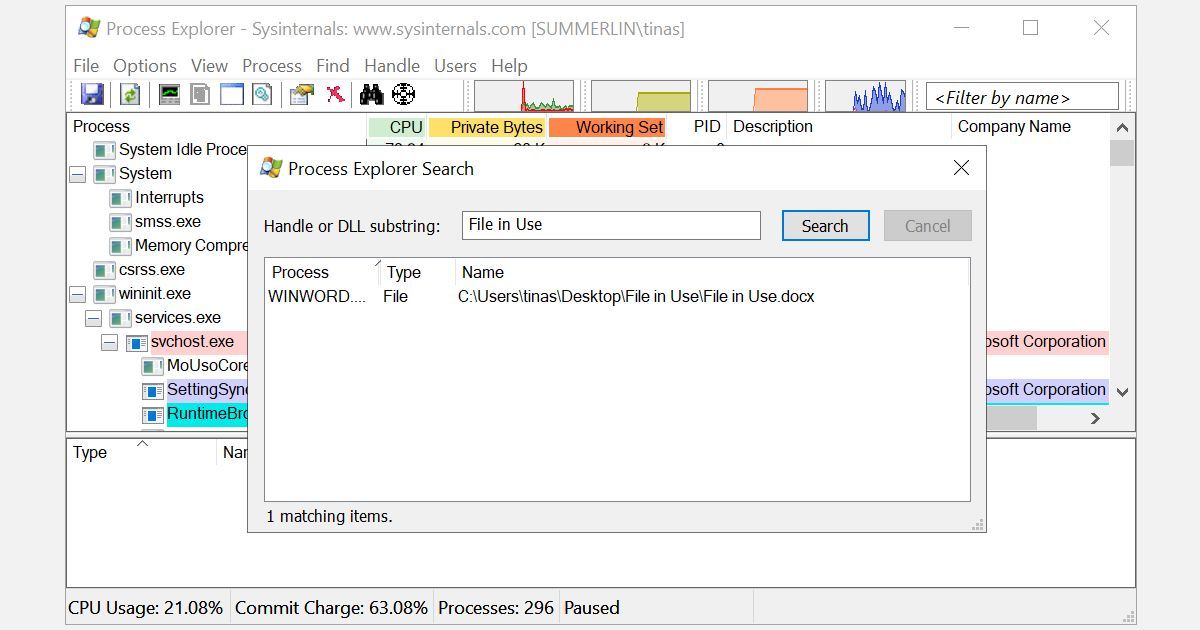
It’s not feasible to terminate the Process from the Search window, but you can use Process Explorer or Windows Task Manager to remove the offending program. Additionally, there are options like this Unlocker And LockHunter , which can help you identify bothersome processes
7. Boot Into Safe Mode
Occasionally, the file you’re trying to delete is automatically downloaded by another app. If that’s the case, apps like Unlocker should still function. If malware is present or you prefer not to use third-party tools, then it’s time to consider other options Booting into Safe Mode Would you consider your next best guess to be accurate?
Press the ENTER arrow on Windows 10 or 11. Win Select the keyboard and place the Power key. Hold the Shift Key and select the Restart Option. After that, your PC will go to the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) page upon startup
Select “Next screen” at the bottom Troubleshoot> Advanced Options> Startup Settings> Restart Upon startup, your computer will display the Startup Settings screen. Choose Safe Mode Wait for the boot up to Windows

In Safe Mode, simply navigate to the appropriate file and try accessing or deleting that file
When Windows indicates that a file is being used, you can either uninstall it or force it off. Using Command Prompt or Safe Mode can help clear up any problems with the file in question, especially if you are not used to using third-party tools