Beyond Reality: How A IR econstructs Light, Shadow and the Unseen
The transformation of reality into a painting by AI involves the use of neural rendering, as illustrated in this video

The use of AI-driven rendering transforms raw video data into photorealistic environments, transforming the way digital imagery is presented
The future of digital realism will not only focus on creating more detailed textures or higher resolutions, but also on mastering the invisible forces of light. The question of how light interacts with objects has eluded both artists and engineers for an extended period. The use of traditional rendering methods involves precise calculations based on physics, but they fail to function in real-world scenarios where accurate data cannot be obtained DIFFUSIONRENDERER is a neural system that surpasses conventional rendering by reconstructing both inverse and forward rendering with unprecedented precision, utilizing AI-powered video diffusion models. The breakthrough has the potential to revolutionize image synthesis across various fields such as game design, CGI, and augmented reality. What is the mechanism behind it, and what makes it so groundbreaking?
Neural reconstruction: Beyond Pixels and Polygons
Neural rendering is not merely an extension of graphics processing, but also a change in the way things are done. Physically based rendering (PBR) and other conventional methods of rendering mimic the interaction between light and 3D geometry. While this method is effective, it requires thorough comprehension of scene parameters, including object geometry, material properties, and light sources. Neural rendering employs patterns learned from large datasets to approximate realistic light transport, even when missing crucial scene data
By utilizing video diffusion models, DIFFUSIONRENDERER reconstructs a photorealistic output and breaks down an image into key scene elements such as surface normals, material roughness, and metallic properties. The use of this method greatly enhances the accuracy of previous 3D rendering methods by reducing the need for precise models, making AI-powered rendering feasible in real-world scenarios where accurate scene data is often unattainable
Double Vision by AI: Forward and Inverse rendering
There are two general types of rendering: forward rendering, which produces realistic images based on given scene information, and inverse rendering (which extracts that information from existing images or videos). With pre-trained video diffusion models, DIFFUSIONRENDERER effortlessly switches between the two modes
The model uses inverse rendering to estimate internal scene characteristics, including geometry, material properties, and lighting conditions. This innovation has revolutionized image editing, eliminating the need for manual scene reconstruction and enabling functions like relighting and object insertion. The use of estimated scene attributes can lead to photorealistic rendering under any lighting conditions through forward rendering. This method is different from traditional rendering, which necessitates accurate physics calculations, as it trains individuals to produce realistic images using training data
Real-time relighting, which allows an image or video to be dynamically manipulated to simulate different lighting conditions without the need for new scene captures, is one of the most powerful applications of this duality. Picture a filmmaker having the ability to instantly convert smoky sunsets into bright midday lighting, or re-blinging in-game illumination without game pre-programming
The Power of Data: Educating AI to See the World
The quality of training data is a crucial factor in the accuracy of neural rendering. DIFFUSIONRENDERER’s training program is a complex combination of both synthetic and physical datasets. Millions of training samples are generated to teach the AI how light behaves by using curated 3D models, environments, and physically based rendering techniques. The inverse rendering model of DIFFUSIONRENDERER is used to extract scene properties from real-world video datasets, which are labeled automatically between synthetic perfection and genuine imperfections
The combination enables the system to generalize across different environments, guaranteeing robust performance, whether it’s reconstructing a photorealistic car interior or estimating the lighting in an outdoor scene. The outcome is an AI that comprehends the physics of image-making and creates intelligent systems
In terms of performance, the DIFFUSIONRENDERER and its competitors are comparable. Traditional Methods
The accuracy of AI-generated results in rendering is a crucial factor to consider when comparing to real-life images. DIFFUSIONRENDERER’s performance is compared to other rendering methods by using PSNR and SSIM:
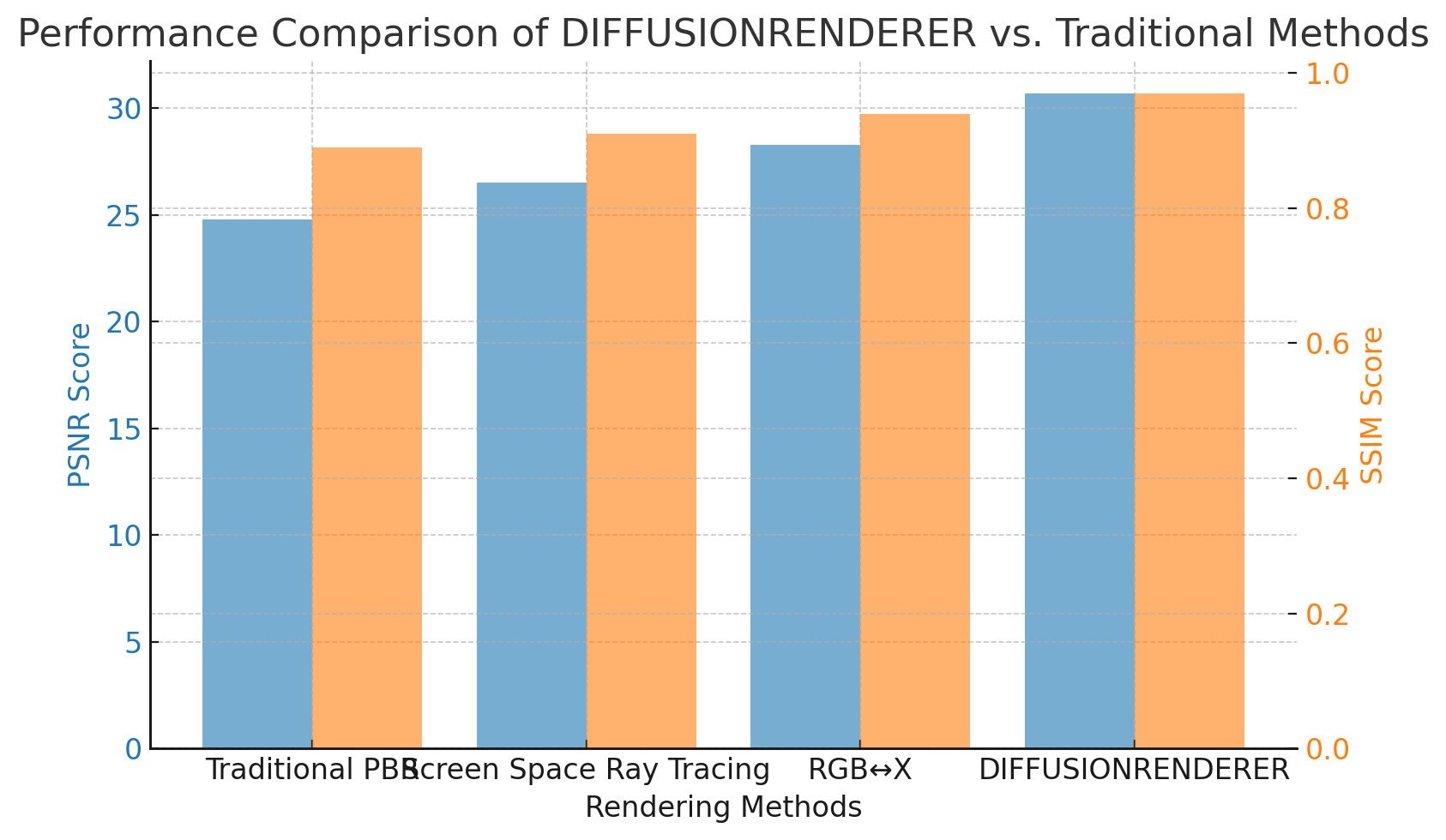
Despite the limitations of current techniques, DIFFUSIONRENDERER is capable of producing photorealistic images with complete scene data
The Artifacts of Light and Shadow Control by AI
Realism is primarily defined by light, and AI has developed the ability to manipulate it in unprecedented ways. The ability of DIFFUSIONRENDERER to predict the direction, intensity, and interaction of light within a scene is essential for relighting and improving visual accuracy in CGI and gaming
The Art of Reverse Engineering Reality:
The ability to use reverse rendering enables AI to extract the essential attributes of an image, such as geometry and texture, from a simple video. The reconstruction of the original lighting environment can be achieved by deciphering these attributes, enabling the seamless placement of virtual objects in real-life footage
The importance of Data in machine Learning and visual analysis
Any intelligent system is built on the basis of data. DIFFUSIONRENDERER is a model that uses both synthetic and real-world datasets to explain the interactions between light in various materials and environments. The AI can render accurately even if input data is flawed
The Untapped Potential of Video Diffusion Models
Video diffusion models differ from traditional image-based models in that they process entire sequences, enabling AI to maintain consistency across multiple frames. In applications like film production, where continuity is crucial, this advancement results in smoother and more realistic outcomes
AN ew Age of Digital Content Creation
Gaming and film industries are not the only beneficiaries of AI-driven rendering. The ability to view objects in dynamic lighting conditions could be advantageous for architectural visualization, fashion design, and online shopping. The ability to rapidly manipulate textures, materials, and light sources signifies the start of a new creative revolution
Unlocking the Future: Applications and Beyond
The arbitrary choice of lighting and materials has wide implications across many industries. Post-production in film and gaming allows directors to relight scenes, while game developers can create more immersive experiences with dynamic lighting. Real-world applications of Augmented and Virtual Reality can incorporate virtual objects with accurate lighting. Various lighting conditions can be used by retailers in e-commerce and design to display their products, enabling customers to visualize furniture or clothing in different settings before purchasing. By utilizing AI-rendered models, scientists can enhance their understanding of light interactions across various materials in fields such as medical imaging and material science
The Road to Success: AI’s Impact on the Visual Revolution
Despite the ongoing development of AI-powered rendering, DIFFUSIONRENDERER is an important step towards becoming photorealistic without using traditional Rendering techniques. The advancement of AI models will result in improved fidelity, real-time performance enhancements, and increased accessibility
The goal is not just to enhance the visual quality of images, but also to alter the way we interact With digital elements
About Disruptive Concepts
Welcome to @Disruptive Concepts Your insight into the future of technology is clear. Subscribe for more insight videos every Saturday!
